MECHANISM OF ACTION SYNOPSIS
- Splenic nerve stimulation is a selective approach to for controlled release of neurotransmitters within the spleen (e.g. noradrenaline)
- These neurotransmitters have been shown to act on macrophages and monocytes to produce immunomodulatory and pro-resolving effects via several pathways important to Rheumatoid Arthritis pathogenesis and resolution
- Immune cells reprogrammed in the spleen then circulate to the of inflammation and injury
HOW IT WORKS
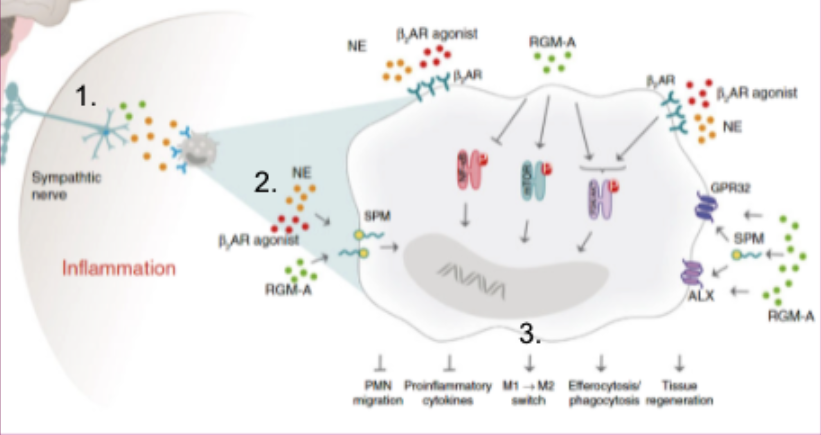
- Direct stimulation of the splenic neurovascular bundle leads to a release of norepinephrine (NE)
- NE release leads to activation of B1/2 adrenergic receptors on myeloid cells
- Myloid cell activation leads to local and system effects including:
- Reduction of multiple pro-inflammatory mediators
- Shift to anti-inflammatory metabolites
- Up-regulation of pro-resolving mediators
- Shift from pathogenic to protective lymphocyte phenotypes
